Two-Stage Probability In Gambling
Tossing Two Coins
The Sample Space for tossing 2 coins can be drawn in 2 ways - tree diagram or table.
Tree Diagram - Sample Space of Tossing 2 Coins
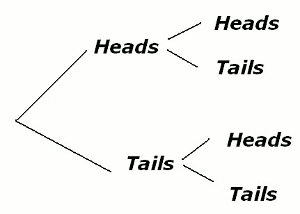
Table - Sample Space of Tossing 2 Coins
| H | T | |
| H | H, H | H, T |
| T | T, H | T, T |
Probabilities of Tossing 2 Coins
Number of outcomes = 2 × 2 = 4
P (2 heads) = 1⁄4
P (1 head) = 2⁄4 = 1⁄2
P (0 heads) = 1⁄4
Tossing Two Dice
The Sample Space for tossing 2 dice can be drawn in a table.
Table - Sample Space of Tossing 2 Dice
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 1 | 1, 1 | 1, 2 | 1, 3 | 1, 4 | 1, 5 | 1, 6 |
| 2 | 2, 1 | 2, 2 | 2, 3 | 2, 4 | 2, 5 | 2, 6 |
| 3 | 3, 1 | 3, 2 | 3, 3 | 3, 4 | 3, 5 | 3, 6 |
| 4 | 4, 1 | 4, 2 | 4, 3 | 4, 4 | 4, 5 | 4, 6 |
| 5 | 5, 1 | 5, 2 | 5, 3 | 5, 4 | 5, 5 | 5, 6 |
| 6 | 6, 1 | 6, 2 | 6, 3 | 6, 4 | 6, 5 | 6, 6 |
Probabilities of Tossing 2 Dice
Number of outcomes = 6 × 6 = 36
P (a total of 1) = 0 (Impossible)
P (a total of 2) = 1⁄36
P (a total of 3) = 2⁄36 = 1⁄18
P (a total of 4) = 3⁄36 = 1⁄12
P (a total of 5) = 4⁄36 = 1⁄9
P (a total of 6) = 5⁄36
P (a total of 7) = 6⁄36 = 1⁄6
P (a total of 8) = 5⁄36
P (a total of 9) = 4⁄36 = 1⁄9
P (a total of 10) = 3⁄36 = 1⁄12
P (a total of 11) = 2⁄36 = 1⁄18
P (a total of 12) = 1⁄36
P (a total of at least 10) = P (a total of 10, 11 or 12) = 6⁄36 = 1⁄6
P ( a total less than 3) = P (a total of 1 or 2) = 1⁄36
P ( a total that is an even number) = P ( a total of 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 or 12) = 18⁄36 = 1⁄2
Maths Fun - Two Dice Game that You Will Almost Always Win!
- The game is about the total of 2 dice.
- You tell your friend that you will be "fair" by having fewer numbers. However, to be "fair", you should choose the numbers first.
- You choose the numbers 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 (only five numbers).
- Your friend then gets the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 10, 11, 12 (seven numbers).
- Remember to bet something substantial e.g. doing the washing up, mowing the grass.
The reason why it works is that:
P (a total of 5, 6, 7, 8 or 9) = 24⁄36 = 2⁄3 and P (1, 2, 3, 4, 10, 11 or 12) = 12⁄36 = 1⁄3
You have twice the chance of winning.
Questions
Q1. In a game where 2 fair coins are tossed, what is probability of throwing:
(a) 2 heads (b) 2 tails (c) only one head?
Q2. In a game where 2 fair dice are tossed, what is probability of throwing:
(a) a total of 7 (b) a difference of 1?
Q3. In a game where 1 coin and 1 die are tossed together, what is the probability of getting a head and a 6?
Answers:
A1. (a) 1⁄4 (b) 1⁄4 (c) 1⁄2
A2. (a) 1⁄6 (b) 2⁄9
A3. 1⁄2 × 1⁄6 = 1⁄12
Example One - Choosing Green and Red Grapes with Replacement

There is a bowl of grapes containing 10 green grapes and 6 red grapes. Without looking, we will pick a grape at a time and then put it back. What is the probability of picking 2 green grapes?
Answer:
P (1st green grape) = 10⁄16 = 5⁄8
P (2nd green grape) = 10⁄16 = 5⁄8
P (2 green grapes with replacement) = 5⁄8 × 5⁄8 = 25⁄64 = 0.39
Example Two - Choosing Green and Red Grapes without Replacement
Frankly, taking grapes of the bunch and replacing them sounds unhygienic! This time when we pick each delicious and healthy grape from the bunch, we will eat it and not replace it!
What is the probability of picking 2 green grapes without looking and without replacement?
Answer:
P (1st green grape) = 10⁄16 = 5⁄8
P (2nd green grape) = 9⁄15 = 3⁄5 (Remember that you already ate 1 green grape.)
P (2 green grapes without replacement) = 5⁄8 × 3⁄5 = 15⁄40 = 0.375
Question
In my socks drawer (which is a mess), there are 1 pair of red socks, 1 pair of blue socks and 1 pair of striped socks. I'm in a hurry to go out and then the electricity blacked out. What is the probability that in the dark and in a hurry I will pick a matching pair?
Answer:
3⁄30 = 1⁄10
Maths Fun
The flags of many nations have only the 3 colours – red, white and blue. If a flag was composed of only 3 equal stripes of red, white and blue (in any order), how many different flags are possible?

| 
| 
|