Parabolas
Before viewing this page, it would be helpful to view the following web pages:

There are 4 graphs that are formed when a cone is sliced by a flat surface. These conic sections are:
- Parabola
- Circle
- Ellipse
- Hyperbola
Parabolic Equations

The U-shaped graph of a quadratic equation in the form of y = ax2 + bx + c is called a parabola.
Examples of parabolas include:
- parabolic mirrors which collect and focus sunlight for solar heating
- radio telescopes which collect radio waves from distant stars
- javelin throwing
- kicking a football through goal posts
- launching a missile
The roots of the equation are the point(s) where the parabola crosses the x-axis. These are the solutions found by factorizing or by using the quadratic formula. There may be two, one or no roots.
The turning point is the point where the graph turns. The formula to find its x-value is:
| x = | –b |
| 2a |
Example One - Graph of y = x2
| x | –3 | –2 | –1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| y = x2 | 9 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 9 |

Example Two - Graph of y = 2x2
| x | –3 | –2 | –1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| y = 2x2 | 18 | 8 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 8 | 18 |

Example Three - Graph of y = 3x2
| x | –3 | –2 | –1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| y = 3x2 | 27 | 12 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 12 | 27 |

Question
Look at the steepness of the graphs of Examples 1, 2 and 3.
What effect does the co-efficient of x2 have on the steepness of the parabola?
Example Four - Graph of y = –x2
| x | –3 | –2 | –1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| y = –x2 | –9 | –4 | –1 | 0 | –1 | –4 | –9 |

Example Five - Graph of y = –2x2
| x | –3 | –2 | –1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| y = –2x2 | –18 | –8 | –2 | 0 | –2 | –8 | –18 |
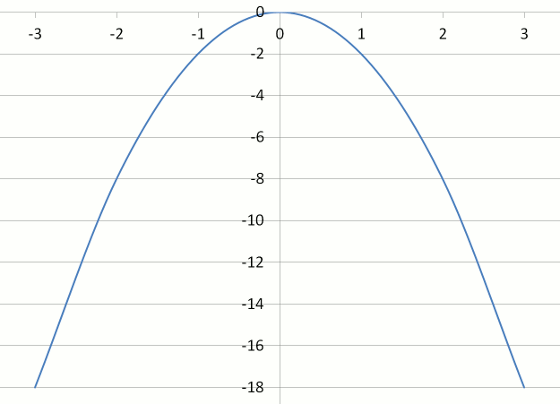
Example Six - Graph of y = –3x2
| x | –3 | –2 | –1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| y = –3x2 | –27 | –12 | –3 | 0 | –3 | –12 | –27 |

Question
Look at the steepness of the graphs of Examples 1 to 6.
What effect does the negative co-efficient of x2 have on the shape of the parabola?
Example Seven - Graph of y = x2 + 3
| x | –3 | –2 | –1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| y = x2 + 3 | 12 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 12 |

Example Eight - Graph of y = x2 – 4
| x | –3 | –2 | –1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| y = x2 – 4 | 5 | 0 | –1 | –4 | –1 | 0 | 5 |
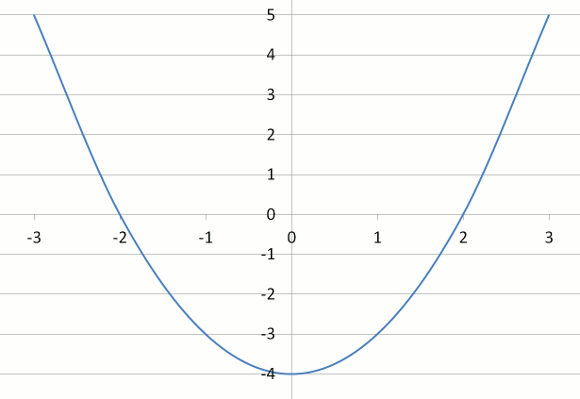
Question
Look at the steepness of the graphs of Examples 1, 7 and 8.
What effect does the constant (i.e. +3 or –3) have on the position of the parabola?
Example Nine - Graph of y = x2 – 6x + 8
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| y = x2 – 6x + 8 | 8 | 3 | 0 | –1 | 0 | 3 | 8 |
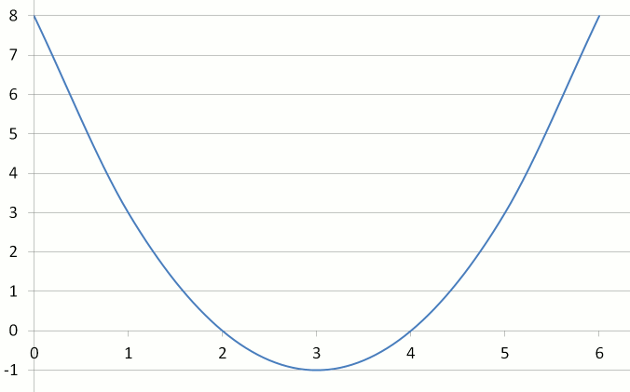
Questions
ROOTS
When you solve the quadratic equation y = x2 – 6x + 8 = 0 by factorization or by formula, x = 2 or 4. These are the 2 roots of the equation.
What do you notice about these roots and the points at which the parabola crosses the x-axis?
TURNING POINT
The formula to find the x value of the turning point of the parabola is x = –b/2a.
Use this formula to find the x value where the graph turns. Substitute this x value into the equation y = x2 – 6x + 8 to find the y value of the turning point.
What do you notice?
Did You Know That...?
The S.K.A. (Square Kilometre Array) of radio telescopes in Australia, New Zealand and South Africa consists of numerous parabola-shaped radio telescopes, altogether with a collecting area of 1 square kilometre. When operational in 2020, the universe will be observable ten thousand times faster than is currently possible.
Consider that when we look at the stars, we are looking back in time. The light from distant stars left the star and has been travelling through space for a long time. For example, the light from our Sun takes 8 minutes to reach the Earth. This means that when we look at our Sun, we are observing it as it was 8 minutes ago. What is the origin of the universe(s)?

| 
| 
|